Panoramica
Le differenze neuroanatomiche e funzionali tra l’emisfero sinistro e quello destro sono caratteristiche di ogni cervello. Abbiamo implementato un modello clinico rilevante per comprendere se e come queste asimmetrie cerebrali sono connesse e influenzano il nostro comportamento e la vita di tutti i giorni. I nostri studi genetici combinatori in vivo rivelano connessioni con l’autismo, la depressione e la schizofrenia.
Linee di ricerca
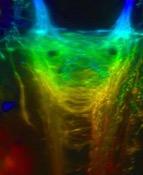
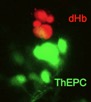
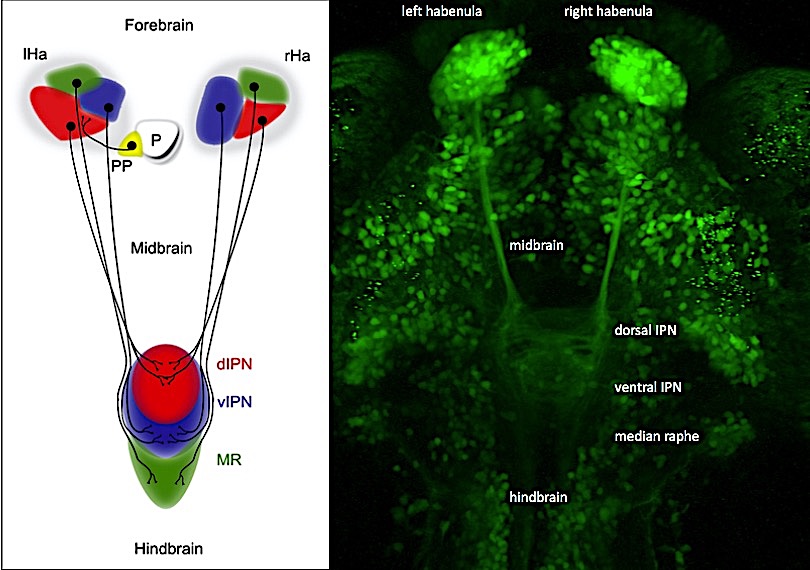
Il sistema di neurotrasmissione abenulare regola diversi tipi di comportamenti, e sue aberrazioni sono state implicate in sindromi patofisiologiche. Potrebbero queste ultime essere legate anche all’asimmetria sinistra-destra del cervello? Come in molti animali, incluso l’uomo, l’abenula nel proencefalo del pesce zebra (Danio rerio) e del pesce del riso (Oryzias latipes), che usiamo principalmente nella nostra ricerca, mostrano differenze sinistra-destra nella dimensione della popolazione neuronale e negli schemi di connettività degli assoni. Abbiamo identificato il pathway Wnt/Beta-catenina come un regolatore chiave dell’asimmetria abenulare. Curiosamente, due dei geni identificati collegano la neurogenesi abenulare con autismo, depressione e schizofrenia. Insieme alla facility di screening ad alta processività del CIBIO abbiamo ora implementato una piattaforma di screening di farmaci in vivo per esplorare ancora più a fondo le reti molecolari responsabili per l’asimmetria cerebrale e, in combinazione con test comportamentali, la sua funzione. Integriamo metodi di analisi genetica, transgenica, molecolare e di imaging per affrontare diversi argomenti:
- Come si origina la diversità neuronale e l’asimmetria cerebrale sinistra-destra?
- Quali sono i collegamenti tra i geni identificati e le malattie mentali?
- L’asimmetria cerebrale influenza il comportamento?
- Screening per identificare farmaci capaci di alleviare le malattie connesse alle reti abenulari.
Membri del gruppo
- Matthias Carl, PI
- Anja Bühler, Post-doc
- Judith Habicher, Post-doc (da Dicembre 2021)
- Studenti triennali e magistrali e ricercatori in visita
Siamo sempre interessati a scienziati altamente motivati, da pre-dottorato fino al post-doc. Potete contattare direttamente il PI Matthias Carl. Mettiamo a disposizione un aiuto sostanziale per la ricerca e per ottenere fondi (e.g. borse).
Collaborazioni
- Risorse sul pesce zebra: Steve Wilson, UCL London, UK
- Geni marker: Myriam Roussigne and Patrick Blader, Université de Toulouse, France
- Strumenti Wnt: Steffen Scholpp, Exeter University, UK
- Transgenica Gene-reporter: Francesco Argenton, University Padova, Italy
- Funzione di Wnt nei moscerini: Veit Riechmann, Heidelberg University, Germany
- Segnalazione di Wnt in colture cellulari: Suat Özbek, Heidelberg University, Germany
- Imaging: Lucia Poggi, Trento University, Italy
- BAC-recombination: Filippo Del Bene, Curie Institute, Paris, France
- Topi con geni di malattie mentali: Giovanni Piccoli, Trento University, Italy
- Risorse sul pesce del riso: Jochen Wittbrodt, Heidelberg University, Germany
- Mutanti e comportamento del pesce del riso: Felix Loosli, KIT, Karlsruhe
Pubblicazioni selezionate
Agostini, C., Bühler, A., Antico Calderone, A., Aadepu, N., Herder, C., Loosli, F. and Carl, M. (2022). Conserved and diverged asymmetric gene expression in the brain of teleosts. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1005776.
Bühler, A. and Carl, M. (2021). Zebrafish tools for deciphering habenular network-linked mental disorders. Biomolecules, 11(2):324
Albadri, S., Armant, O., Aljand-Geschwill, T., Del Bene, F., Carl, M., Strähle, U., Poggi, L. (2020). Expression of a Barhl1a reporter in subsets of retinal ganglion cells and commissural neurons of the developing zebrafish brain. Scientific Reports, 10(1):8814.
Guglielmi, L., Bühler, A., Moro, E., Argenton, F., Poggi, L. and Carl, M. Temporal control of Wnt signaling is required for habenular neuron diversity and brain asymmetry (2020). Development, 147(6), doi: 10.1242/dev.182865.
Imle, R., Wang, B.T., Stützenberger, N., Birkenhagen, J., Tandon, A., Carl, M., Himmelreich, N., Thiel, C., Gröne, H.J., Poschet, G., Völkers, M., Gülow, K., Schröder, A., Carillo, S., Mittermayr, S., Bones, J., Kamiński, M.M., Kölker, S., Sauer, S.W. (2019). ADP-dependent glucokinase regulates energy metabolism via ER-localized glucose sensing. Scientific Reports, 9(1):14248.
Breuer, M., Guglielmi, L., Zielonka, M., Hemberger, V., Kölker, S., Okun, J.G., Hoffmann, G.F., Carl, M. #, Sauer, S.W. #, Opladen, T. # (2019). Qdpr homologues in Danio rerio regulate melanin synthesis, early gliogenesis, and glutamine homeostasis. Plos One, 14(4):e0215162. (#equal contribution)
Zielonka, M., Probst, J., Carl, M., Hoffmann, G.F., Kölker, S., Okun, J.G. (2019). Bioenergetic dysfunction in a zebrafish model of acute hyperammonemic decompensation. Experimental Neurology, 314:91-99.
Poggi, L., Casarosa, S., Carl, M. (2018). An eye on the Wnt inhibitory factor Wif1. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 6:167
Roussigné, M.; Wei, L., Tsingos, E., Kuchling, F., Alkobtawi, M., Tsalavouta, M., Witbrodt, J.W., Carl, M., Biader, P., Wilson, S.W. (2018). Left/right asymmetric collettive migration of parapineal cells is mediated by focal FGF signalling activity in leading cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 115(42):E9812-E9821.
Zielonka, M., Breuer, M., Okun, J.G., Carl, M., Hoffmann, G. F., Kölker, S. (2018). Pharmacologic rescue of hyperammonemia-induced toxicity in zebrafish by inhibition of ornithine aminotransferase. PlosOne, 13(19):e023707.
Dimitrov, B., Himmelreich, N., Hipgrave Ederveen, A.L., Lüchtenborg, C., Okun, J.O., Breuer, M., Hutter, A.-M., Carl, M., Guglielmi, L., Hellwig, A., Thiemann, K.C., Jost, M., Peters, V., Staufner, C., Hoffmann, G.F., Hackenberg, A., Paramasivam, N., Wiemann, S., Eils, R., Schlesner, M., Strahl, S., Brügger, B., Wuhrer, M., Korenke, G.C., and Thiel, C. (2018). Cutis laxa, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency and altered cellular metabolism as additional symptoms in a new patient with ATP6AP1-CDG. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism, 123(3):364-374.
Choi, J.-H., Jeong, Y.-M., Kim, S., Lee, B., Ariyasiri, K., Kim, H.-T., Jung, S.-H., Seung, Hwang, K.-S., Choi, T.-I., Park, C.O., Huh, W.-H., Carl, M., Rosenfeld, J.A., Raskin, S., Ma, A., Gecz, J., Kim, H.-G., Kim, J.-S., Shin, H.-C., Park, D.-S., Gerlai, R., Jamieson, B.B., Kim, J.S., Iremonger, K.J., Lee, S.H., Shin, H.-S., Kim, C.-H. (2018). Targeted knockout of a chemokine-like gene increases anxiety and fear responses. PNAS, 115(5):E1041-E1050.
Cepero Malo, M., Duchemin, A.-L., Guglielmi, L., Patzel, E., Sel, S., Auffarth, G.U., Carl, M., and Poggi, L. (2017). The zebrafish Anillin-eGFP reporter marks late dividing retinal precursors and stem cells entering neuronal lineages. PlosOne, 12(1):e0170356.
Beretta, C.A., Dross, N., Guglielmi, L., Bankhead, P., Soulika, M., Gutierrez-Triana, J.A., Paolini, A., Poggi, L., Falk, J., Ryu, S., Kapsimali, M., Engel, U., Carl, M. (2017). Early commissural diencephalic neurons control habenular axon extension and targeting. Current Biology, 27:270-278.
Kopajtich, R., Murayama, K., Janecke, A.R., Haack, T.B., Breuer, M., Knisely, A.S., Harting, I., Ohashi, T., Okazaki, Y., Watanabe, D., Tokuzawa, Y., Kotzaeridou, U., Kölker, S., Sauer, S., Carl, M., Straub, S., Entenmann, A., Gizewski, E., Feichtinger, R.G., Mayr, J.A., Lackner, K., Strom, T.M., Meitinger, T., Müller, T., Ohtake, A., Hoffmann, G.F., Prokisch, H., Staufner, C. (2016). Biallelic mutations in IARS, encoding cytosolic isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase, cause growth retardation with prenatal onset, intellectual disability, muscular hypotonia, and infantile hepatopathy. American Journal of Human Genetics, 99:414-422.
Beretta, C.A., Dross, N., Engel, U., and Carl, M. (2016). Tracking cells in GFP-transgenic zebrafish using the photoconvertible PSmOrange system. J. Vis. Exp. (108), e53604.
Hüsken, U., Stickney, H.L., Gestri, G., Bianco, I.H., Faro, A., Young, R.M., Roussigne, M., Hawkins, T.A., Beretta, C.A., Brinkmann, I., Paolini A., Jacinto, R., Albadri, S., Dreosti, E., Tsalavouta, M., Schwarz, Q., Cavodeassi, F., Barth, A.K., Wen, L., Zhang, B., Blader, P., Yaksi, E., Poggi, L., Zigman, M., Lin, S., Wilson, S.W., and Carl, M. (2014). Tcf7l2 is required for left-right asymmetric differentiation of habenular neurons. Current Biology 24(19):2217-2227.
Dross, N., Beretta, C.A., Bankhead, P., Carl, M., and Engel, U. (2014). Zebrafish Brain Development Monitored by Long-Term in Vivo Microscopy: A Comparison Between Laser Scanning Confocal and 2-Photon Microscopy. Book Title: Laser Scanning Microscopy and Quantitative Image Analysis of Neuronal Tissue. Springer Science.
Dreosti, E., Llopis, N.V., Carl, M., Yaksi E., and Wilson, S.W. (2014). Left/right asymmetry is required for the habenulae to respond to both visual and olfactory stimuli. Current Biology 24(4):440-445.
Mwafi, N., Beretta, C.A., Paolini, A., and Carl, M. (2014). Divergent Wnt8a gene expression in teleosts. Plos One 9(1):e85303.
Beretta, C.A., Dross, N., Bankhead, P., and Carl, M. (2013). The ventral habenulae in zebrafish develop in prosomere 2 dependent on Tcf7l2 function. Neural Development 8(1):19.
Demir, K., Kirsch, N., Beretta, C.A., Erdmann, G., Ingelfinger, D., Moro, E., Argenton, F., Carl, M., Niehrs, C., and Boutros, M. (2013). RAB8B is required for activity and caveolar endocytosis of LRP6. Cell Reports 4(6):1224-1234.
Hüsken, U. and Carl, M. (2013). The Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway establishes neuroanatomical asymmetries and their laterality. Mech. Dev. 130: 330-335.
McNabb, A., Scott, K., von Ochsenstein, E., Seufert, K. and Carl, M. (2012). Don’t be afraid to set up your fish facility. Zebrafish 9(3): 120-125.
Beretta, C.A., Dross, N., Guiterrez-Triana, J.A., Ryu, S. and Carl, M. (2012). Habenula circuit development: past, present, and future. Frontiers in Neuroscience 6:51.
Berns, N., Woichansky, I., Kraft, N., Hüsken, U., Carl, M. and Riechmann, V. (2012). „Vacuum-assisted staining“: a simple and efficient method for screening Drosophila. Dev. Genes Evol. 222: 113-118.
Beretta, C.A., Brinkmann, I. and Carl, M. (2011). All four zebrafish Wnt7 genes are expressed during early brain development. Gene Expression Patterns 11: 277-284.
Wilkinson, C.J., Carl, M. and Harris, W.A. (2009). Cep70 and Cep131 contribute to ciliogenesis in zebrafish embryos. BMC Cell Biology 10:17.
Bianco, I.H., Carl, M., Russell, C., Clark, J. and Wilson, S.W. (2008). Brain asymmetry is encoded at the level of axon terminal morphology. Neural Development 3: 9.
Carl, M., Bianco, I.H., Bajoghli, B., Aghaallaei, N., Czerny, T., and Wilson, S.W. (2007). Wnt/Axin1/b-catenin signaling regulates asymmetric nodal activation, elaboration, and concordance of CNS asymmetries. Neuron 55(3): 393-405.
Yokoi, H., Shimada, A., Carl, M., Takashima, S., Kobayashi, D., Narita, T., Jindo, T., Kimura, T., Kitagawa, T., Kage, T., Sawada, A., Naruse, K., Asakawa, S., Shimizu, N., Mitani, H., Shima, A., Tsutsumi, M., Hori, H., Wittbrodt, J., Saga, Y., Ishikawa, Y., Araki, K., and Takeda, H. (2007). Mutant analyses reveal different functions of fgfr1 in medaka and zebrafish despite conserved ligand-receptor relationships. Dev. Biol. 304(1): 326-337.
Hochmann, S., Aghaallaei, N., Bajoghli, B., Soroldoni, D., Carl, M., and Czerny, T. (2007). Expression of marker genes during early ear development in medaka. Gene Expression Patterns 7(3): 355-362.
