Overview
Neuroanatomical and functional differences between the left and right brain hemisphere are characteristics of every brain. We established a clinically relevant model system to elucidate if and how these brain asymmetries are connected and influence our daily life and behavior. Our combinatorial in vivo genetic studies reveal links to autism, depression and schizophrenia.
Research directions
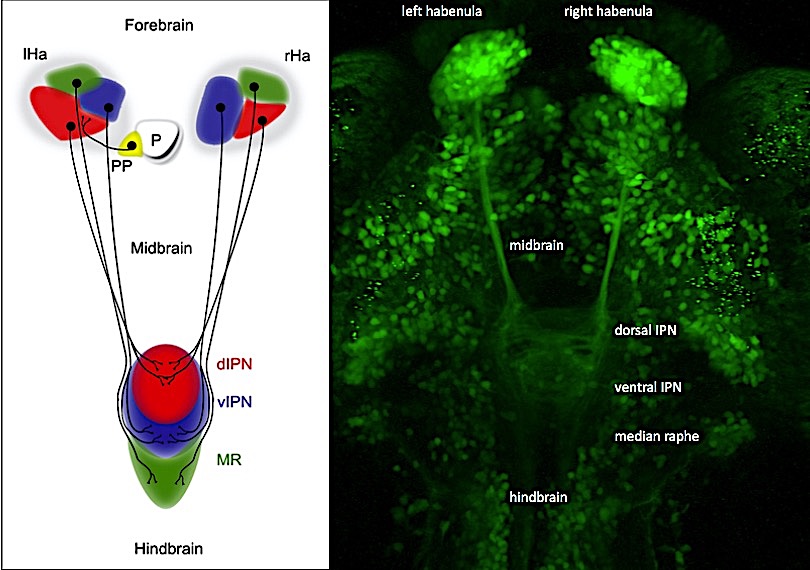
The conserved habenular neurotransmitter system regulates various behaviors and aberrations have been implicated in pathophysiological syndromes – but are these also linked to left-right brain asymmetry? Like in most animals including humans, the habenulae in the forebrain of zebrafish (Danio rerio) and medakafish (Oryzias latipes), which we mainly use for our research, exhibit left-right differences in the size of neuronal populations and axonal connectivity patterns. We have identified the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway as a key regulator of the establishment of habenular asymmetry. Intriguingly, two of the genes discovered link habenular neurogenesis with autism, depression and schizophrenia. Together with CIBIO’s high throughput screening facility we have now established an in vivo drug screening platform to further dissect the molecular networks underlying brain asymmetry and, in combination with behaviour testing, its function. We combine genetic, transgenic, molecular and imaging methods for research on the following topics:
- How is neuronal diversity and left-right brain asymmetry established?
- What are the links between the genes uncovered and mental illness?
- Does brain asymmetry influence behavior?
- Screening for drugs ameliorating habenular network related diseases.
Group members
- Matthias Carl, PI (link to website)
- Anja Bühler, Post-doc
- Judith Habicher, Post-doc (from December 2021)
- Fluctuating Bachelor- and Master students as well as visiting researchers
We are always interested in highly motivated scientists from undergraduate student to postdoc level. Please contact directly the PI Matthias Carl. Substantial help for research and raising funds (fellowships etc.) is available.
Collaborations
- Resources for zebrafish: Steve Wilson, UCL London, UK
- Marker genes: Myriam Roussigne and Patrick Blader, Université de Toulouse, France
- Wnt tools: Steffen Scholpp, Exeter University, UK
- Gene-reporter transgenics: Francesco Argenton, University Padova, Italy
- Wnt function in fly: Veit Riechmann, Heidelberg University, Germany
- Wnt signaling in cell culture: Suat Özbek, Heidelberg University, Germany
- Imaging: Lucia Poggi, Trento University, Italy
- BAC-recombination: Filippo Del Bene, Curie Institute, Paris, France
- Mental disease genes mouse: Giovanni Piccoli, Trento University, Italy
- Medaka resources: Jochen Wittbrodt, Heidelberg University, Germany
- Medaka mutants and behavior: Felix Loosli, KIT, Karlsruhe
Selected publications
Habicher, J.; Sanvido, I.; Bühler, A.; Sartori, S.; Piccoli, G.; Carl, M. (2024). The risk genes for neuropsychiatric disorders negr1 and opcml are expressed throughout zebrafish brain development. Genes, 15:363. https://doi.org/10.3390/
Agostini, C., Bühler, A., Antico Calderone, A., Aadepu, N., Herder, C., Loosli, F. and Carl, M. (2022). Conserved and diverged asymmetric gene expression in the brain of teleosts. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1005776.
Bühler, A. and Carl, M. (2021). Zebrafish tools for deciphering habenular network-linked mental disorders. Biomolecules, 11(2):324
Albadri, S., Armant, O., Aljand-Geschwill, T., Del Bene, F., Carl, M., Strähle, U., Poggi, L. (2020). Expression of a Barhl1a reporter in subsets of retinal ganglion cells and commissural neurons of the developing zebrafish brain. Scientific Reports, 10(1):8814.
Guglielmi, L., Bühler, A., Moro, E., Argenton, F., Poggi, L. and Carl, M. Temporal control of Wnt signaling is required for habenular neuron diversity and brain asymmetry (2020). Development, 147(6), doi: 10.1242/dev.182865.
Imle, R., Wang, B.T., Stützenberger, N., Birkenhagen, J., Tandon, A., Carl, M., Himmelreich, N., Thiel, C., Gröne, H.J., Poschet, G., Völkers, M., Gülow, K., Schröder, A., Carillo, S., Mittermayr, S., Bones, J., Kamiński, M.M., Kölker, S., Sauer, S.W. (2019). ADP-dependent glucokinase regulates energy metabolism via ER-localized glucose sensing. Scientific Reports, 9(1):14248.
Breuer, M., Guglielmi, L., Zielonka, M., Hemberger, V., Kölker, S., Okun, J.G., Hoffmann, G.F., Carl, M. #, Sauer, S.W. #, Opladen, T. # (2019). Qdpr homologues in Danio rerio regulate melanin synthesis, early gliogenesis, and glutamine homeostasis. Plos One, 14(4):e0215162. (#equal contribution)
Zielonka, M., Probst, J., Carl, M., Hoffmann, G.F., Kölker, S., Okun, J.G. (2019). Bioenergetic dysfunction in a zebrafish model of acute hyperammonemic decompensation. Experimental Neurology, 314:91-99.
Poggi, L., Casarosa, S., Carl, M. (2018). An eye on the Wnt inhibitory factor Wif1. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 6:167
Roussigné, M.; Wei, L., Tsingos, E., Kuchling, F., Alkobtawi, M., Tsalavouta, M., Witbrodt, J.W., Carl, M., Biader, P., Wilson, S.W. (2018). Left/right asymmetric collettive migration of parapineal cells is mediated by focal FGF signalling activity in leading cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 115(42):E9812-E9821.
Zielonka, M., Breuer, M., Okun, J.G., Carl, M., Hoffmann, G. F., Kölker, S. (2018). Pharmacologic rescue of hyperammonemia-induced toxicity in zebrafish by inhibition of ornithine aminotransferase. PlosOne, 13(19):e023707.
Dimitrov, B., Himmelreich, N., Hipgrave Ederveen, A.L., Lüchtenborg, C., Okun, J.O., Breuer, M., Hutter, A.-M., Carl, M., Guglielmi, L., Hellwig, A., Thiemann, K.C., Jost, M., Peters, V., Staufner, C., Hoffmann, G.F., Hackenberg, A., Paramasivam, N., Wiemann, S., Eils, R., Schlesner, M., Strahl, S., Brügger, B., Wuhrer, M., Korenke, G.C., and Thiel, C. (2018). Cutis laxa, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency and altered cellular metabolism as additional symptoms in a new patient with ATP6AP1-CDG. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism, 123(3):364-374.
Choi, J.-H., Jeong, Y.-M., Kim, S., Lee, B., Ariyasiri, K., Kim, H.-T., Jung, S.-H., Seung, Hwang, K.-S., Choi, T.-I., Park, C.O., Huh, W.-H., Carl, M., Rosenfeld, J.A., Raskin, S., Ma, A., Gecz, J., Kim, H.-G., Kim, J.-S., Shin, H.-C., Park, D.-S., Gerlai, R., Jamieson, B.B., Kim, J.S., Iremonger, K.J., Lee, S.H., Shin, H.-S., Kim, C.-H. (2018). Targeted knockout of a chemokine-like gene increases anxiety and fear responses. PNAS, 115(5):E1041-E1050.
Cepero Malo, M., Duchemin, A.-L., Guglielmi, L., Patzel, E., Sel, S., Auffarth, G.U., Carl, M., and Poggi, L. (2017). The zebrafish Anillin-eGFP reporter marks late dividing retinal precursors and stem cells entering neuronal lineages. PlosOne, 12(1):e0170356.
Beretta, C.A., Dross, N., Guglielmi, L., Bankhead, P., Soulika, M., Gutierrez-Triana, J.A., Paolini, A., Poggi, L., Falk, J., Ryu, S., Kapsimali, M., Engel, U., Carl, M. (2017). Early commissural diencephalic neurons control habenular axon extension and targeting. Current Biology, 27:270-278.
Kopajtich, R., Murayama, K., Janecke, A.R., Haack, T.B., Breuer, M., Knisely, A.S., Harting, I., Ohashi, T., Okazaki, Y., Watanabe, D., Tokuzawa, Y., Kotzaeridou, U., Kölker, S., Sauer, S., Carl, M., Straub, S., Entenmann, A., Gizewski, E., Feichtinger, R.G., Mayr, J.A., Lackner, K., Strom, T.M., Meitinger, T., Müller, T., Ohtake, A., Hoffmann, G.F., Prokisch, H., Staufner, C. (2016). Biallelic mutations in IARS, encoding cytosolic isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase, cause growth retardation with prenatal onset, intellectual disability, muscular hypotonia, and infantile hepatopathy. American Journal of Human Genetics, 99:414-422.
Beretta, C.A., Dross, N., Engel, U., and Carl, M. (2016). Tracking cells in GFP-transgenic zebrafish using the photoconvertible PSmOrange system. J. Vis. Exp. (108), e53604.
Hüsken, U., Stickney, H.L., Gestri, G., Bianco, I.H., Faro, A., Young, R.M., Roussigne, M., Hawkins, T.A., Beretta, C.A., Brinkmann, I., Paolini A., Jacinto, R., Albadri, S., Dreosti, E., Tsalavouta, M., Schwarz, Q., Cavodeassi, F., Barth, A.K., Wen, L., Zhang, B., Blader, P., Yaksi, E., Poggi, L., Zigman, M., Lin, S., Wilson, S.W., and Carl, M. (2014). Tcf7l2 is required for left-right asymmetric differentiation of habenular neurons. Current Biology 24(19):2217-2227.
Dross, N., Beretta, C.A., Bankhead, P., Carl, M., and Engel, U. (2014). Zebrafish Brain Development Monitored by Long-Term in Vivo Microscopy: A Comparison Between Laser Scanning Confocal and 2-Photon Microscopy. Book Title: Laser Scanning Microscopy and Quantitative Image Analysis of Neuronal Tissue. Springer Science.
Dreosti, E., Llopis, N.V., Carl, M., Yaksi E., and Wilson, S.W. (2014). Left/right asymmetry is required for the habenulae to respond to both visual and olfactory stimuli. Current Biology 24(4):440-445.
Mwafi, N., Beretta, C.A., Paolini, A., and Carl, M. (2014). Divergent Wnt8a gene expression in teleosts. Plos One 9(1):e85303.
Beretta, C.A., Dross, N., Bankhead, P., and Carl, M. (2013). The ventral habenulae in zebrafish develop in prosomere 2 dependent on Tcf7l2 function. Neural Development 8(1):19.
Demir, K., Kirsch, N., Beretta, C.A., Erdmann, G., Ingelfinger, D., Moro, E., Argenton, F., Carl, M., Niehrs, C., and Boutros, M. (2013). RAB8B is required for activity and caveolar endocytosis of LRP6. Cell Reports 4(6):1224-1234.
Hüsken, U. and Carl, M. (2013). The Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway establishes neuroanatomical asymmetries and their laterality. Mech. Dev. 130: 330-335.
McNabb, A., Scott, K., von Ochsenstein, E., Seufert, K. and Carl, M. (2012). Don’t be afraid to set up your fish facility. Zebrafish 9(3): 120-125.
Beretta, C.A., Dross, N., Guiterrez-Triana, J.A., Ryu, S. and Carl, M. (2012). Habenula circuit development: past, present, and future. Frontiers in Neuroscience 6:51.
Berns, N., Woichansky, I., Kraft, N., Hüsken, U., Carl, M. and Riechmann, V. (2012). „Vacuum-assisted staining“: a simple and efficient method for screening Drosophila. Dev. Genes Evol. 222: 113-118.
Beretta, C.A., Brinkmann, I. and Carl, M. (2011). All four zebrafish Wnt7 genes are expressed during early brain development. Gene Expression Patterns 11: 277-284.
Wilkinson, C.J., Carl, M. and Harris, W.A. (2009). Cep70 and Cep131 contribute to ciliogenesis in zebrafish embryos. BMC Cell Biology 10:17.
Bianco, I.H., Carl, M., Russell, C., Clark, J. and Wilson, S.W. (2008). Brain asymmetry is encoded at the level of axon terminal morphology. Neural Development 3: 9.
Carl, M., Bianco, I.H., Bajoghli, B., Aghaallaei, N., Czerny, T., and Wilson, S.W. (2007). Wnt/Axin1/b-catenin signaling regulates asymmetric nodal activation, elaboration, and concordance of CNS asymmetries. Neuron 55(3): 393-405.
Yokoi, H., Shimada, A., Carl, M., Takashima, S., Kobayashi, D., Narita, T., Jindo, T., Kimura, T., Kitagawa, T., Kage, T., Sawada, A., Naruse, K., Asakawa, S., Shimizu, N., Mitani, H., Shima, A., Tsutsumi, M., Hori, H., Wittbrodt, J., Saga, Y., Ishikawa, Y., Araki, K., and Takeda, H. (2007). Mutant analyses reveal different functions of fgfr1 in medaka and zebrafish despite conserved ligand-receptor relationships. Dev. Biol. 304(1): 326-337.
Hochmann, S., Aghaallaei, N., Bajoghli, B., Soroldoni, D., Carl, M., and Czerny, T. (2007). Expression of marker genes during early ear development in medaka. Gene Expression Patterns 7(3): 355-362.
